Scientists have created artificial skin that helps wounds heal quickly
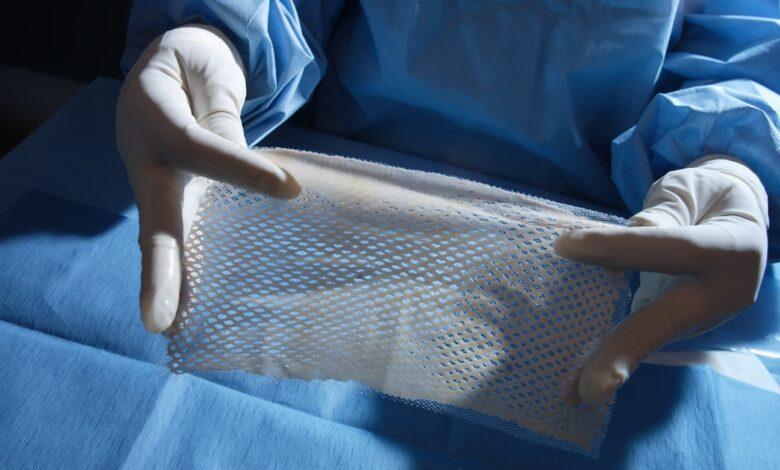
Israeli scientists have created artificial skin in the laboratory, which they plan to use to treat patients with burns. It has greater elasticity compared to other types of artificial leather and promotes much faster healing of wounds. About this it is said in a study published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
“Surgery is often necessary for second-degree and higher burns to repair the skin, prevent infection, and save lives. Currently, the gold standard of treatment is autologous skin grafting, where healthy skin is taken from another part of the patient’s body and transferred to the burn site.”, — explains professor Ligi Adler-Abramovich.
According to him, this method has serious limitations, because it requires damage to healthy tissues to treat the affected area, and in the case of significant skin damage, there is often nowhere to get healthy areas.
In the Shiba Medical Center, the search for alternative solutions began. Researchers have developed a “cultured epidermal autograft”, which is grown in the laboratory from the patient’s own cells. The advantage of the method is that a small amount of donor cells is needed to create artificial skin.
“We designed a nanofibrous scaffold made of PCL polymer and combined it with a bioactive peptide, a short sequence of amino acids that stimulates cell growth and proliferation. We then ‘seeded’ this scaffold with skin cells obtained from a patient’s biopsy. Impressively, the cells self-organized to mimic the structure of real human skin.”, — said researcher Dana Cohen-Herassi.
Another researcher, Marina Ben-Shonan, emphasizes that the graft provides faster healing of burns:
“Our graft is unique in that it is strong, flexible and easy to use. Implantation has produced impressive results. In standard treatment, it takes eight days to close half of a burn wound, in our case it takes only four. In addition, we observed the growth of important skin structures such as hair follicles.”
At the same time, the method has certain drawbacks. In particular, many grafts are required to cover large affected areas. For example, up to 30 grafts are needed to cover one arm or leg. In the future, the researchers plan to conduct additional tests to determine the most effective ways to apply the new technology.





