The annual resources of the Earth are exhausted: humanity lives in debt, starting from August 1

Every year, humanity consumes more resources than the planet can regenerate. Recently, we live as if we have at our disposal not one Earth, but 1.75 planets. Every year we borrow more and more from her. Every year, the day when humanity’s annual supply of resources is completely exhausted comes earlier and earlier. This year it fell on August 1. What does it mean? As for the remaining days until the new year, i.e. the conventional reference point for the new annual portion of resources, we live in debt.
Calculation of the date of “Environmental Debt Day” (Earth Overshoot Day) is carried out by the Global Footprint Network organization.
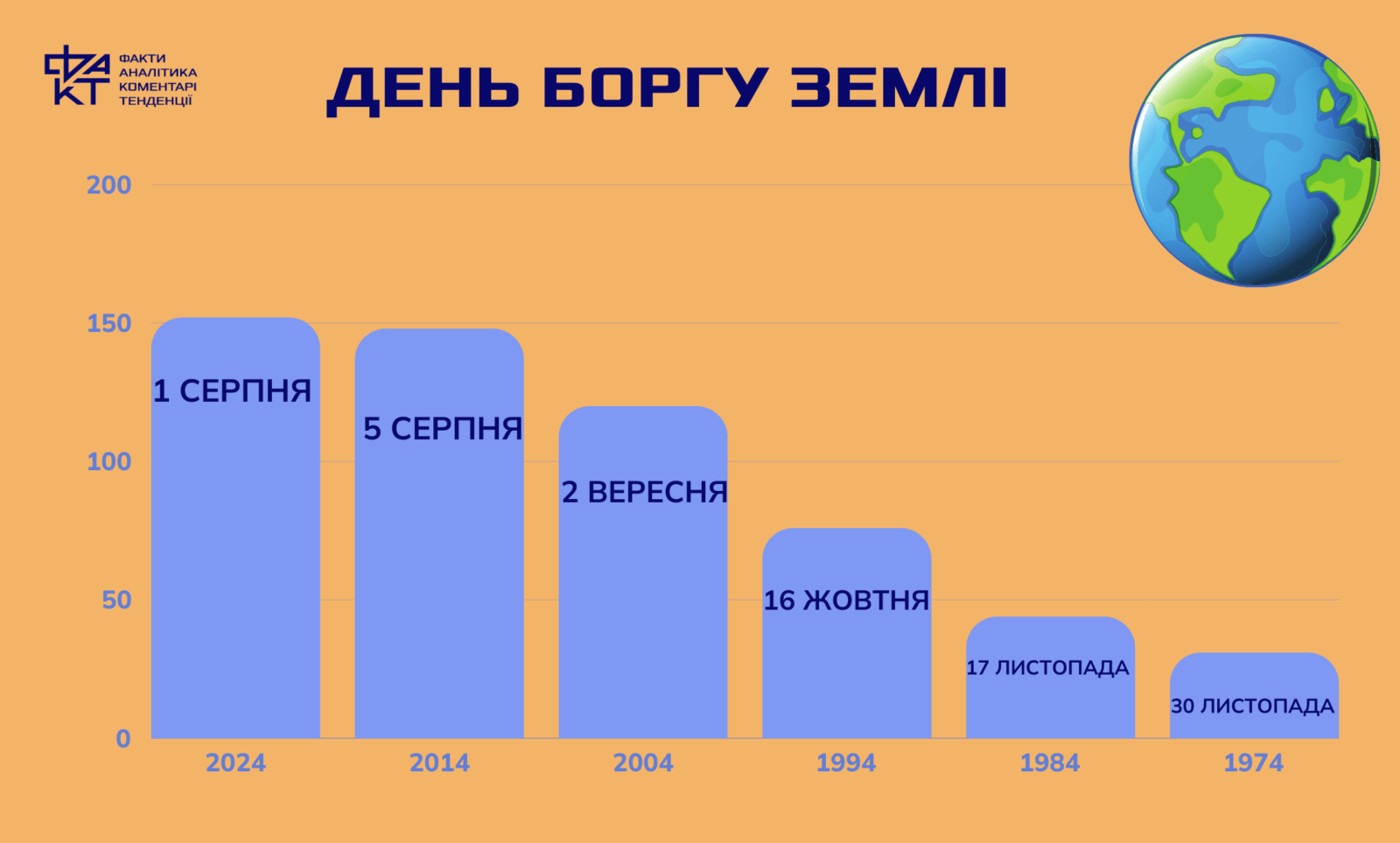
According to her, last year this day came on August 2, so in the current year humanity “dealt” with the Earth’s reserves a day earlier.
How is the calculation carried out?
To determine the Earth’s Exceeding Day date for each year, the Global Footprint Network calculates the number of days in the current year when the Earth’s biocapacity is sufficient to sustain humanity’s ecological footprint. The remainder of the year corresponds to a global excess. Earth’s excess day is calculated by dividing the planet’s biocapacity (the amount of ecological resources the Earth is capable of renewing in a year) by humanity’s ecological footprint (humanity’s demand for that year) and multiplying by 365 or 366 days, like now in the leap year 2024.
Personal “Earth Debt Day” everyone can calculate independently, using the appropriate calculator. By the way, my result is disappointing: if all people lived like me, we would need 8.2 planets every year. So, there is reason to think.
What resources does humanity consume the least economically?
The excess of Earth’s resources includes the use of agricultural land and wood. The ability of our planet to absorb garbage and emissions is beyond the limit of recovery.
Overfishing has also become a serious problem. Over time, it will lead to a decrease in fish populations and disrupt the ecological balance in the oceans and seas. Overfishing can also affect fishing communities that depend on fishing as their main source of income. Decreasing fish stocks can lead to reduced fishing profits and threaten people’s livelihoods.
Those that fly are harmful
According to Germanwatch, a relatively small part of the world’s population that often uses air transport, is one of the main factors of the climate crisis.
For example, more than 60% of Germans indicate that they fly only occasionally or do not use airplanes when traveling. If we talk about the scale of humanity, 80% of the world’s population has never flown.
So, we are talking about a really small segment of the world’s humanity, which flies because it can afford it, and probably does not think about the fact that it causes climatic damage to the earth.
Why are airplanes considered particularly harmful in this sense? They cause three times the greenhouse effect compared to the same amount of CO₂ emitted on land, Germanwatch notes. One of the reasons is contrails – clouds formed behind airplanes at high altitude. They occur when water vapor emitted from aircraft exhaust pipes condenses into small ice crystals or water droplets due to low temperature and high humidity. Such clouds can affect the heat exchange in the atmosphere, trapping the heat that comes from the Earth. This is a significant factor in increasing global warming.
On the other hand, when it comes to Europe, rail transport is a more ecological alternative, as it is up to 28 times more “climate-friendly” than intra-European flights.
And to the good news
However, ecologists have good news. And it is that, although we continue to consume more resources than the planet can regenerate, the rate of this excess has recently stabilized. This gives hope that with the introduction of renewable energy sources, storage technologies, electromobility and heat pumps, we can begin to reduce our consumption of resources and thus avoid climate tipping points and biodiversity loss.
An interesting point. The so-called “covid” year 2022, when humanity seemed to freeze under the pressure of the pandemic and significantly reduced its activities, owed the least to the Earth. Debt Day that year fell on August 16. We draw conclusions.





